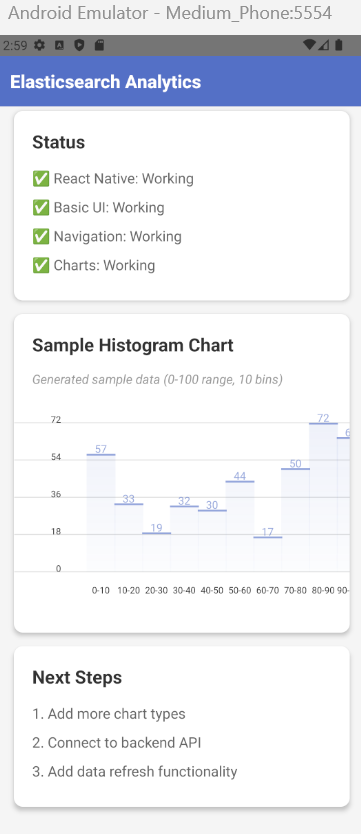
MobileAPP for Elasticsearch ?


Welcome to soyacoffee

Query: What is LlamaIndex?
Average response time: 11.04 seconds
LlamaIndex is an open source project developed by DeepSeeK Labs that provides a comprehensive solution for managing and querying large amounts of structured and unstructured data efficiently. It offers vector indexing, parallel processing, query caching, and supports various data sources including text files, PDFs, web pages, databases, and APIs. The platform is designed to be scalable and flexible for high-performance data management in LLM applications.
Query: How does LlamaIndex help with data processing?
Average response time: 24.70 seconds
LlamaIndex improves data processing by providing:
These features collectively enhance performance and scalability for handling large datasets in LLM applications.
Query: What are the main features of LlamaIndex?
Average response time: 24.44 seconds
Query: How can LlamaIndex improve response time?
Average response time: 7.79 seconds
These mechanisms enable LlamaIndex to return faster and more accurate results from large datasets.
Query: What data sources does LlamaIndex support?
Average response time: 2.25 seconds
import numpy as np
# y = wx + b
def cal_err_linear_given_points(b, w, points):
totalErr = 0
for i in range (0, len (points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
totalErr += (y - (w * x + b)) ** 2
return totalErr / float (len (points))
def step_grad(b_current, w_current, points, learnRate):
b_grad = 0
w_grad = 0
N = float (len (points))
for i in range (0, len (points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[1, 1]
b_grad += -(2 / N) * (y - ((w_current * x) + b_current))
w_grad += -(2 / N) * x * (y - ((w_current * x) + b_current))
new_b = b_current - (learnRate * b_grad)
new_w = w_current - (learnRate * w_grad)
return [new_b, new_w]
# iterate to optimize
def grad_descent_exe(points, starting_b, starting_w, learnRate, num_iterations):
b = starting_b
w = starting_w
for i in range (num_iterations):
b, w = step_grad (b, w, np.array (points), learnRate)
print (b, w)
return [b, w]
def exe():
points = np.genfromtxt ("data.csv", delimiter=",")
# print(points)
learnRate = 0.0001
initial_b = 0 # guessing y-intercept
initial_w = 0 # guessing slope
num_iterations = 1000
print ("Starting grad descent at b = {0}, m = {1}, err = {2}"
.format (initial_b, initial_w, cal_err_linear_given_points (initial_b, initial_w, points)))
[b, w] = grad_descent_exe (points, initial_b, initial_w, learnRate, num_iterations)
print ("After {0} interations b = {1}, m = {2}, err = {3}"
.format (num_iterations, b, w, cal_err_linear_given_points (b, w, points)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
exe ()
Let’s learn about list comprehensions! You are given three integers x, y, z and representing the dimensions of a cuboid along with an integer n . Print a list of all possible coordinates given by on a 3D grid where the sum of is not equal to n . Please use list comprehensions rather than multiple loops
Example
x = 1
y = 1
z= 2
n = 3
All permutations of [i,j,k] are:
[[0,0,0], [0,0,1], [0,0,2], [0,1,0],[0,1,1]………..]
Print an array of the elements that do not sum to n.
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('Please enter value x :')
x = int(input())
print('Please enter value y :')
y = int(input())
print ('Please enter value z :')
z = int(input())
print('Please enter elements that do not sum to:')
n = int(input())
print([[i, j, k] for i in range(0, x+1) for j in range(0, y+1) for k in range(0,z +1) if i+j+k != n])
Happy Chinese New Year to you and your family! I hope this year will bring the warmth of love and positivity in your life.
祝大家身体健康,财源广进,牛气冲天,牛转乾坤!

Welcome to WordPress. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start writing!